Digital vs Optical Zoom: Which Is Better?
-
 Written by:
Kristy Roger
Written by:
Kristy Roger
- Last Updated:
Are you wondering about the difference between Digital and Optical Zoom? In this article, projector expert Kristy Roger shares her knowledge on Digital vs. Optical Zoom comparison, with pictures of each and easy day-to-day life examples!
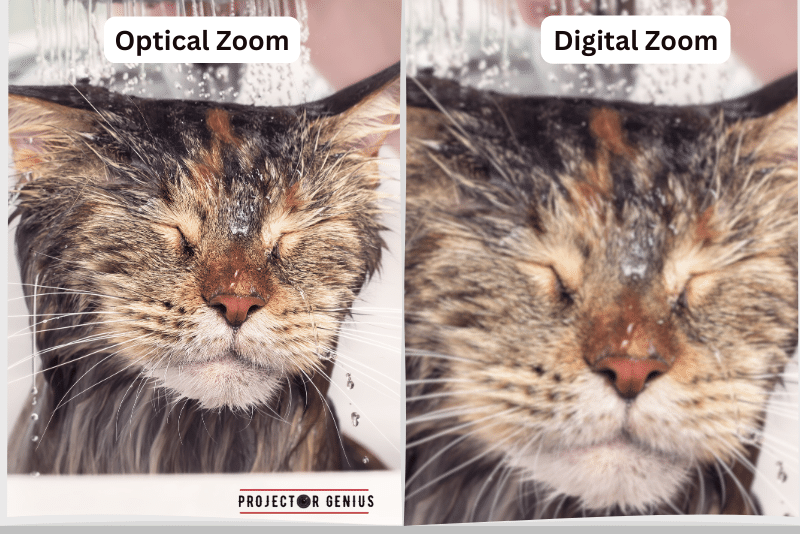
Digital vs Optical Zoom? Digital zoom is not as good as optical zoom. Optical zoom uses the camera’s lens to magnify the image, preserving image quality, while digital zoom enlarges the image electronically, leading to a loss of quality. Therefore, optical zoom is generally better for maintaining image clarity.
I recommend using the Table of Contents to quickly access the information you need.
My article is designed to cater to home cinema users of all levels, from Beginners to Advanced enthusiasts.
Table of Contents
Digital vs Optical Zoom in Projectors
When it comes to Projectors, zooming capability plays a crucial role in adjusting the image size and positioning without physically moving the Projector. There are two main types of zoom technology used in Projectors: digital zoom and optical zoom. Let’s explore the differences between digital and optical zoom and their implications for image quality.
Digital Zoom
It is a software-based zooming technique that enlarges or reduces the image size by cropping and interpolating the pixels. When you use digital zoom, the Projector magnifies the existing pixels to create the illusion of a larger image. However, this process can lead to a loss of image quality and resolution since the Projector is essentially “stretching” the pixels to fit the desired size.
Pros of Digital Zoom
Convenient: Digital zoom is often available on most Projectors and can be easily accessed through the remote control or on-screen menu.
Cost-effective: Implementing digital zoom does not require additional optical components, making it more budget-friendly.
Cons of Digital Zoom
Image Quality: Digital zoom can result in a decrease in image sharpness and clarity due to the interpolation of pixels.
Pixelation: As the image is digitally enlarged, pixelation may occur, making the image appear blocky or less defined.
Optical Zoom
It is a hardware-based zooming technique that adjusts the image size by physically moving the lens elements. When you use optical zoom, the lens expands or contracts, maintaining the image resolution and clarity throughout the zoom range. This is because the Projector is optically magnifying or reducing the image projected onto the screen without sacrificing image quality.
Pros of Optical Zoom
Image Quality: Optical zoom preserves the image’s original resolution and sharpness, ensuring high-quality visuals.
Versatility: The ability to zoom optically allows for greater flexibility in Projector placement, as the image size can be adjusted without moving the Projector itself.
Cons of Optical Zoom
Cost and Complexity: Implementing optical zoom requires specialized lens components, which can increase the Projector’s cost and complexity.
Difference between Digital vs Optical Zoom in Projectors
The choice between digital and optical zoom depends on your priorities and the level of image quality you desire. If convenience and cost are crucial factors, digital zoom may suffice for basic zooming needs. However, for applications where image quality is paramount, optical zoom is preferred.
Optical zoom ensures that the projected image remains clear and detailed, offering a superior viewing experience for presentations, movies, and other visual content. When selecting a Projector, consider the zooming capabilities and determine which type of zoom aligns with your specific requirements and expectations.
Comparison of Projector Optical Zoom vs. Digital Zoom
When it comes to Projector zooming capabilities, there are significant differences between optical zoom and digital zoom. Let’s compare these two types of zooming in terms of brightness, resolution, and contrast ratio:
1. Brightness
Optical Zoom: Optical zoom does not affect the Projector’s brightness. When you use optical zoom to adjust the image size, the amount of light remains the same, and the brightness of the projected image remains constant. This is because optical zoom physically adjusts the lens elements without altering the light intensity.
Digital Zoom: Digital zoom, on the other hand, can impact the Projector’s brightness. When you use digital zoom to enlarge the image, the same amount of light is spread over a larger area, resulting in a potential reduction in brightness. This means that the projected image may appear dimmer when digital zoom is used extensively.
2. Resolution
Optical Zoom: Optical zoom maintains the Projector’s native resolution throughout the zoom range. Since the lens physically adjusts to magnify or reduce the image, there is no loss of image resolution. The Projector displays the content pixel-for-pixel, ensuring sharp and clear visuals regardless of the zoom level.
Digital Zoom: Digital zoom can affect the image resolution. When you use digital zoom to enlarge the image, the Projector interpolates the existing pixels, which can lead to a decrease in image quality. The image may appear pixelated or less defined when significant digital zooming is applied.
3. Contrast Ratio
Optical Zoom: Optical zoom does not alter the Projector’s contrast ratio. The contrast ratio remains constant throughout the zoom range since optical zoom adjusts the lens elements without affecting the light output or black levels.
Digital Zoom: Digital zoom does not directly impact the contrast ratio. However, it may indirectly affect perceived contrast due to changes in image size and brightness. When using digital zoom to enlarge the image, the perceived contrast between dark and bright areas may be affected, especially if the brightness is reduced.
In summary, optical zoom offers advantages over digital zoom in terms of brightness, resolution, and contrast ratio. Optical zoom maintains consistent brightness, native resolution, and contrast throughout the zoom range, ensuring optimal image quality and visual performance. On the other hand, digital zoom may lead to potential reductions in brightness, image resolution, and perceived contrast due to its software-based interpolation of pixels. When image quality and performance are essential, optical zoom is the preferred choice for achieving the best projection results.
Which is Better Digital Zoom or Optical Zoom?
Optical zoom is Better Than Digital Zoom.
1. Image Quality of Optical Zoom
Optical zoom preserves the original resolution and clarity of the image throughout the zooming process. It physically adjusts the lens elements to magnify or reduce the image, ensuring no loss of detail. On the other hand, digital zoom relies on software interpolation, which can result in a decrease in image quality and sharpness. As the pixels are digitally manipulated, the image may appear pixelated or less defined.
2. Versatility of Optical Zoom
Optical zoom provides greater flexibility in Projector placement. You can adjust the image size without moving the Projector physically. This versatility is particularly useful in different environments or when precise image adjustments are required. Digital zoom, while convenient, lacks the same level of flexibility as it does not physically alter the image projection.
3. Pixelation and Artifacts of Optical Zoom
Digital zoom can introduce pixelation and visual artifacts, especially when enlarging the image significantly. The interpolation of pixels can cause the image to appear blocky or jagged, affecting the overall visual appeal. Optical zoom, on the other hand, ensures a smooth and clear image without such distortions.
4. Image Control of Optical Zoom
Optical zoom offers precise and real-time image control. You can make adjustments smoothly and accurately with no loss of quality. Digital Zoom, being a software-based process, may have limitations in providing the same level of precise control.
5. Cost and Performance of Optical Zoom
While digital zoom is often more cost-effective since it doesn’t require additional optical components, the trade-off is a potential compromise in image quality. Optical zoom may involve a slightly higher initial cost, but it delivers superior performance and maintains image integrity.
In summary, optical zoom is considered better than digital zoom due to its ability to preserve image quality, offer greater versatility in Projector placement, and provide superior control over image adjustments.
While digital zoom may be more convenient and budget-friendly, it is not recommended for situations where image quality is a top priority.
For critical applications such as professional presentations, home theatres, or any scenario where high-quality visuals matter, optical zoom is the preferred choice to ensure an exceptional viewing experience.
Does Optical Zooming Reduce Picture Quality?
No, optical zooming does not reduce picture quality. In fact, optical zoom is specifically designed to maintain the original resolution and clarity of the image while adjusting the image size. When you use optical zoom, the Projector physically moves the lens elements to magnify or reduce the image, ensuring that the projected content remains sharp and detailed.
Unlike digital zoom, which relies on software interpolation and can lead to a decrease in image quality, optical zoom works without any loss of detail. The physical adjustment of the lens in optical zoom allows the Projector to maintain the same level of image integrity throughout the zoom range.
With optical zoom, you can enlarge or reduce the image size without sacrificing image quality. This makes optical zoom the preferred choice for situations where preserving the highest image clarity and sharpness is essential, such as professional presentations, home theatres, or any application where picture quality matters.
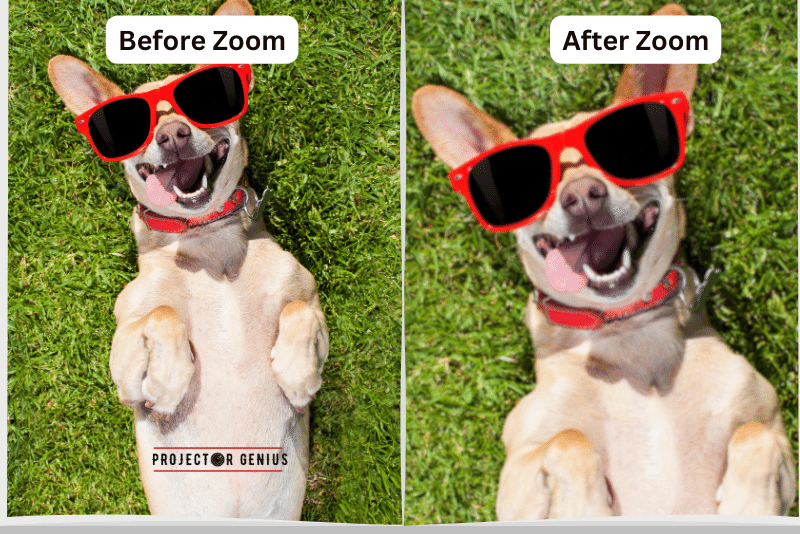
When Should you use a Digital Zoom?
You should use a digital zoom when you have no other option for adjusting the image size, and you understand the potential trade-offs in image quality.
Digital zoom is a software-based technique that enlarges or reduces the image size by digitally manipulating the pixels. It can be useful in certain situations, but it’s important to be aware of its limitations:
1. Limited Optical Zoom
If your Projector does not have optical zoom capabilities or has limited zoom range, and physically adjusting the Projector’s placement is not feasible, digital zoom can be a workaround to achieve a larger or smaller image size.
2. Minor Adjustments
Digital zoom can be suitable for making minor adjustments to the image size when precise control over the zoom is not critical. For example, slight adjustments to fit the content on the screen without significant loss of image quality.
3. Image Cropping
If you need to focus on a specific portion of the image or want to crop out unwanted elements, digital zoom can be handy for achieving this effect.
Potential Drawbacks of Using Digital Zoom
Image Quality Loss
Digital zoom relies on software interpolation, which can lead to a decrease in image quality. The process of digitally enlarging the image can result in pixelation, making the image appear less sharp and defined.
Limited Precision
Unlike optical zoom, which offers precise control over image adjustments, digital zoom can lack the same level of precision and may not provide optimal results for fine-tuning image size.
Best Used Sparingly
It’s best to use digital zoom sparingly and only when absolutely necessary, as repeated use of digital zoom for significant enlargements can significantly degrade the image quality.
In summary, use digital zoom when you have no other option for adjusting the image size, but be mindful of its impact on image quality. If possible, it’s always preferable to use optical zoom or physically adjust the Projector’s placement to maintain the highest image clarity and sharpness. Digital zoom can be a useful tool for minor adjustments, but for critical applications where image quality matters, optical zoom is the preferred choice.
Should You Place Your Projector to Minimize Zoom?
Placing your Projector to minimize zoom is generally recommended for achieving the best image quality and optimal viewing experience.
When you minimize zoom, you are essentially using the Projector’s native resolution and displaying the content at its original size. This means that each pixel of the input signal directly corresponds to a pixel on the Projector’s display, resulting in a clear and sharp image with no loss of detail. It allows the Projector to project the content in its native resolution without any scaling or digital manipulation.
Several reasons why minimizing Zoom is beneficial
- Image Quality: Using the native resolution of the Projector ensures the highest image quality. It avoids the potential image degradation that can occur with digital zoom, which relies on software interpolation and may lead to pixelation and reduced clarity.
- Brightness: Minimizing zoom often results in a brighter image. When you use Zoom to enlarge the image, the same amount of light is spread over a larger area, leading to a potential reduction in brightness. By minimizing zoom, you can maximize the Projector’s brightness and ensure a more vibrant and vivid display.
- Optimal Viewing Distance: Placing the Projector to minimize zoom helps determine the ideal viewing distance for your setup. When the image is displayed in its native resolution, you can calculate the best distance for the audience to have a comfortable and immersive viewing experience.
- Simplified Setup: Minimizing Zoom simplifies the setup process. You don’t need to worry about adjusting zoom levels, and it reduces the need for precise adjustments.
However, it’s essential to consider the room size and the desired screen size when placing the Projector. Make sure to position the Projector at an appropriate distance from the screen to achieve the desired image size while minimizing zoom. If the Projector placement is limited due to room constraints, and zooming becomes necessary to fit the screen, try to use optical zoom rather than digital zoom to maintain image quality.
Final Thoughts
In summary, optical zoom offers advantages over digital zoom in terms of brightness, resolution, and contrast ratio. Optical zoom maintains consistent brightness, native resolution, and contrast throughout the zoom range, ensuring optimal image quality and visual performance.
On the other hand, digital zoom may lead to potential reductions in brightness, image resolution, and perceived contrast due to its software-based interpolation of pixels. When image quality and performance are essential, optical zoom is the preferred choice for achieving the best projection results.
Author of this Post:

Kristy Roger
Home Cinema Consultant & Tech Enthusiast
Holding a background in Industrial and Electrical Technology from the University of Alberta, Kristy has spent 5+ years consulting on home theater products at a top electronics firm. As a certified Technical Professional with Lean Six Sigma credentials, Kristy expertise ranges from projector nuances to hands-on experience with leading models. Kristy have been sharing her knowledge online for two years, blending professional insights with personal experiences from her own home cinema setup. Off the screen, She is a dedicated mom to Jerry, Ryan, and our two pups, Cuddle and Paw.