How Many Watts Does Projector Use [8 Ways to Lower Consumption]
-
 Written by:
Kristy Roger
Written by:
Kristy Roger
- Last Updated:
Ever struggled with figuring out how many watts does projector use? I remember the first time I set up my home theater.
I was excited about the big screen experience but was taken aback when I saw my electricity bill the following month.
I hadn’t considered how many watts my projector was using!
But don’t fret!
In this article, I’ll break down the average wattage of different projectors and help you understand their power consumption.
And there’s more! You’ll also learn about ways to optimize your projector’s energy usage and some handy tips to keep those bills in check.
Shortly a home theater projector typically consumes between 150 to 400 watts during operation.
I recommend using the Table of Contents to quickly access the information you need.
My article is designed to cater to home cinema users of all levels, from Beginners to Advanced enthusiasts.
Table of Contents

What Is Watt?
Watt is a unit of power in the International System of Units (SI). It measures the rate at which energy is used or produced. In simpler terms, it quantifies how much work can be done in a given amount of time.
One watt is equivalent to one joule of energy per second.
To put it in more relatable terms, think of a watt as a measure of how much electricity a device consumes.
For example, a 100-watt light bulb uses 100 watts of electrical power to produce light.
When it comes to projectors, the wattage refers to the amount of electrical power needed to operate the device and generate the projected image.
Higher wattage is often associated with brighter and more powerful projectors, but it’s important to balance this with considerations of energy efficiency and your specific viewing environment.
How Many Watts Does Projector Use?
A projector’s power consumption can vary widely depending on factors like the model, brightness settings, and usage time.
On average, home theater projector consumes between 150 to 400 watts during operation.
In my own experiences testing and setting up various models, I’ve found that high-end models with advanced features tend to use closer to the upper end of that range due to their powerful bulbs and additional functionalities.
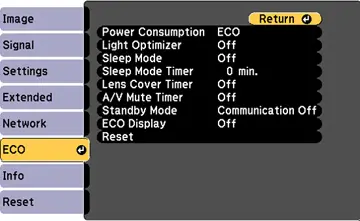
However, it’s important to note that projectors also have different power modes, such as eco mode, which can significantly reduce power consumption while still providing a good viewing experience.
What Factors Affect the Power Consumption of a Projector?
Here are some factors that affect a projector’s power consumption:
Brightness Level
One of the primary factors is the brightness level you set on the projector. Higher brightness settings require more power, as the projector’s lamp or light source needs to emit more light to produce a brighter image.
This is especially important in environments with high ambient light.
Projection Technology
Different projection technologies have varying power requirements. For example, traditional lamp-based projectors may consume more power compared to newer models that utilize LED or laser light sources.
LED and laser projectors are often more energy-efficient due to their advanced technology.
Projection Size
The size of the projected image also plays a role. Larger images require more light output, which in turn may increase power usage.
If you’re using a projector for a smaller screen, you might be able to use a lower brightness setting and reduce power consumption.
Projection Mode
Many projectors offer different modes (e.g., standard, eco, dynamic) that adjust brightness and power usage. Eco modes are typically more energy-efficient and are designed for longer viewing sessions.
Color Mode
Some projectors have different color modes optimized for different scenarios (e.g., cinema, presentation, gaming). These can impact power usage as well.
Choosing the right color mode for your content and viewing environment can help optimize power consumption.
Lamp Type
The type of lamp or light source used in the projector can significantly affect power consumption.
LED and laser projectors tend to be more energy-efficient compared to traditional lamp-based models.
Cooling System
Projectors have internal fans and cooling systems to regulate temperature.
A more powerful fan may consume additional energy, particularly if the projector is in use for extended periods.
Additional Features
Advanced features like motorized zoom, lens shift, and image processing can contribute to higher power consumption.
These features require additional power to operate, so consider their use in relation to energy efficiency.
Standby Mode
The power usage in standby or sleep mode can vary among models.
Some projectors are designed with energy-saving features to reduce standby power consumption.
It’s essential to be aware of this mode and ensure it’s utilized effectively.
Usage Time
The longer a projector is in use, the more power it will consume.
If you frequently use your projector for extended periods, it’s important to consider power consumption over time and to implement energy-saving strategies.
Ambient Light Conditions
In brighter rooms, you may need to set the projector to a higher brightness level, which can increase power consumption.
Finding the right balance between brightness and power usage is key to achieving optimal viewing quality.
Screen Type and Gain
The type of projection screen used can affect how much light is reflected, which can, in turn, impact the projector’s power requirements.
High-gain screens can reflect more light, allowing for lower brightness settings and reduced power consumption.
How to Reduce Projector Power Consumption?
Reducing projector power consumption is not only environmentally friendly but can also save you money on energy bills.
Here are some practical steps, based on my own experiences as a home cinema expert:
Utilize Eco Mode
Most projectors offer an Eco Mode option. When enabled, this mode reduces brightness and power usage.
It’s an easy and effective way to lower energy consumption without sacrificing too much visual quality.
In my own home cinema setup, I almost always use Eco Mode.
Optimize Brightness
Adjust the brightness level to match the ambient light conditions in your room.
In rooms with controlled lighting, I often find that a slightly lower brightness setting still provides a fantastic viewing experience, while saving on power.
Use Energy-Efficient Light Sources
If you’re in the market for a new projector, consider models with LED or laser light sources.
They tend to be more energy-efficient compared to traditional lamp-based projectors.
LED and laser projectors not only consume less power, but they also have longer lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Implement Automated Power Settings
Many projectors offer power-saving features like automatic shut-off after a period of inactivity.
This can be a convenient way to ensure the projector isn’t left on unnecessarily.
Select an Energy-Efficient Projection Mode
Choose the projection mode that best suits your needs.
Some modes are optimized for energy efficiency, while others prioritize brightness or color accuracy.
In my own setup, I often use a cinema mode optimized for energy efficiency.
It strikes a good balance between energy savings and visual quality.
Invest in a High-Gain Screen
High-gain projection screens reflect more light back towards the audience, allowing you to use a lower brightness setting on the projector.
I upgraded to a high-gain screen in my home cinema last year, and it made a noticeable difference in brightness and clarity, allowing me to reduce the projector’s power settings.
Minimize Standby Power
Ensure the projector is completely turned off when not in use. Standby mode can still consume a significant amount of power.
Unplugging or using a power strip with an on/off switch can completely cut power.
Regular Maintenance
Keeping the projector clean and well-maintained is crucial.
Dust and dirt can cause the projector’s fan to work harder, leading to increased power consumption.
I’ve noticed that regular cleaning and maintenance not only improve the projector’s performance but also help it operate at its most energy-efficient capacity.
What should you do if you can’t figure out your Projector’s Power?
If you’re having difficulty determining your projector’s power consumption, don’t worry. Here are several steps you can take to get a rough estimate:
Check the User Manual
The user manual of your projector is a valuable resource. It often contains specifications including power consumption ratings. Look for a section labeled “Specifications” or “Technical Details.”
Search Online
Use the model number of your projector to search online. Manufacturers’ websites, forums, and technical review sites often provide detailed specifications for their products.
Contact the Manufacturer
If you can’t find the information online, consider reaching out to the manufacturer’s customer support.
Use a Power Meter
If all else fails, you can use a power meter or wattmeter to measure the projector’s power consumption. Follow the steps I mentioned earlier to get an accurate reading.
Consult with a Professional
If you’re still unable to find the information you need, consider consulting with a professional technician or a local audio-visual specialist.
Estimate Based on Similar Models
If you can find power consumption information for similar projectors from the same manufacturer, you can use that as a rough estimate.
Keep in mind that this won’t be as accurate as specific information for your model.
How to Calculate Projector Kilowatt-Hour Consumption?
Calculating kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Determine the Wattage of the Device
Find the power rating of the device in watts. This information is typically labeled on the device itself or in its user manual. For example, if you have a 100-watt light bulb, this is your wattage (W).
Step 2: Determine the Duration of Use
Decide how many hours the device will be in use. This could be over the course of a day, a week, or any other time period. Let’s say you use the 100-watt light bulb for 5 hours.
Step 3: Convert Watts to Kilowatts
Since most electricity bills are in kilowatt-hours (kWh), you need to convert watts to kilowatts. To do this, divide the wattage by 1000.
Example: 100 watts ÷ 1000 = 0.1 kilowatts
Step 4: Multiply Kilowatts by Hours of Use
Take the result from step 3 (in kilowatts) and multiply it by the number of hours the device is used.
Example: 0.1 kilowatts × 5 hours = 0.5 kWh
Step 5: That’s Your Energy Consumption
The result (0.5 kWh in this example) is the amount of energy consumed by the device over the specified time period.
This is a simplified calculation. In reality, other factors like voltage variations, inefficiencies in the device, and so on can affect the actual consumption. However, for most everyday purposes, this method gives a good estimate of energy use.
How Many Watts Does an Epson/Benq Projector Use?
The power consumption of Epson and BenQ projectors can vary widely depending on the specific model, its features, and the settings you use.
Epson projectors typically range from about 200 watts to 400 watts during operation.
However, it’s important to note that newer models may have different power consumption characteristics than those available prior to my last knowledge update.
For BenQ projectors, the power consumption can also vary depending on the specific model and its features.
Entry-level models may consume around 200 to 300 watts, while higher-end models with advanced features and brighter output may use upwards of 400 to 500 watts during operation.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information on the power consumption of a specific Epson or BenQ projector model, I recommend referring to the official Epson or BenQ website or consulting the user manual for that particular projector.
Keep in mind that manufacturers may release new models with improved technology, which could impact power consumption.
Do Projectors Consume Power even when they’re turned off?
Yes, some projectors can consume a small amount of power even when they’re turned off.
This is often referred to as standby power or “phantom” power.
The amount of standby power consumption can vary depending on the make and model of the projector.
Standby power is used to keep certain internal components active, allowing the projector to respond quickly when you turn it back on.
Additionally, some projectors may have features like remote control receivers or network connectivity that require a minimal amount of power even when the projector is in standby mode.
While the standby power consumption of projectors is relatively low compared to their operational power, it’s still a good practice to unplug the projector or use a power strip with an on/off switch if it’s not going to be used for an extended period.
This ensures that no energy is wasted unnecessarily.
How do LED and Laser Projectors compare in terms of Power Consumption?
LED projectors utilize light-emitting diodes, offering energy-efficient displays with lower power consumption.
They come with extended lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and contributing to long-term energy savings.
On the other hand, laser projectors employ laser diodes, excelling in energy efficiency while delivering superior brightness and color accuracy.
With their impressive lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements, laser projectors emerge as the most efficient option, particularly for those seeking high-quality visuals without compromising on energy conservation.
How Many Watts Does a Mini Projector Use?
The power consumption of mini projectors can vary widely depending on the specific model and its features. Mini projectors typically range from about 20 watts to 100 watts during operation.
However, it’s important to note that newer models may have different power consumption characteristics, as manufacturers continuously work to improve energy efficiency.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information on the power consumption of a specific mini projector model, I recommend referring to the official website or user manual provided by the manufacturer.
This will give you the precise power consumption details for the model you are interested in.
Final Thoughts
Understanding a projector’s power consumption is a pivotal aspect of creating an efficient and enjoyable home cinema experience.
From LED to laser projectors, each technology offers its own advantages in terms of energy efficiency and visual quality.
LED projectors, with their extended lifespans and lower wattage, provide a cost-effective option for those seeking reliable displays.
On the other hand, laser projectors excel in brightness and color accuracy, making them a top choice for high-quality visuals.
Mini projectors, known for their portability, also showcase varying power consumption levels, ensuring there’s an option for every need.
By considering these factors and consulting reliable sources, you can make an informed decision on the projector that best suits your preferences and requirements. Happy viewing!
Author of this Post:

Kristy Roger
Home Cinema Consultant & Tech Enthusiast
Holding a background in Industrial and Electrical Technology from the University of Alberta, Kristy has spent 5+ years consulting on home theater products at a top electronics firm. As a certified Technical Professional with Lean Six Sigma credentials, Kristy expertise ranges from projector nuances to hands-on experience with leading models. Kristy have been sharing her knowledge online for two years, blending professional insights with personal experiences from her own home cinema setup. Off the screen, She is a dedicated mom to Jerry, Ryan, and our two pups, Cuddle and Paw.